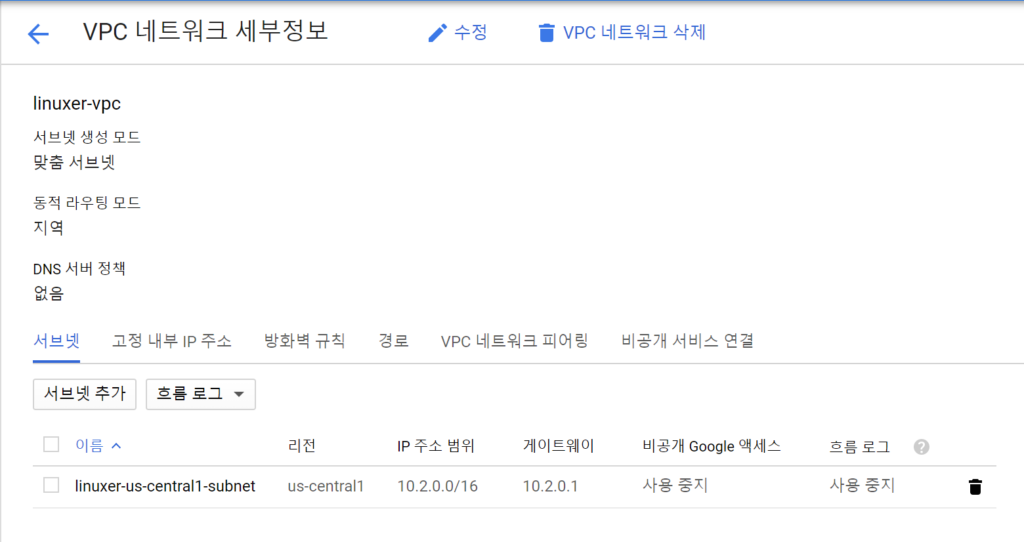
EFS를 사용하고 백업/복구 이야기를 하려고한다.
EFS는 NFS기반의 편리한 서비스다. aws backup로 스냅샷 방식의 백업이 가능하다.

현재 측정크기가 6.0kib인데
# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 475M 0 475M 0% /dev
tmpfs 492M 0 492M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 492M 404K 492M 1% /run
tmpfs 492M 0 492M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/xvda1 8.0G 4.6G 3.5G 57% /
tmpfs 99M 0 99M 0% /run/user/0
fs-7eb4fb1f.s.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com:/ 8.0E 0 8.0E 0% /mnt/efs
root@ip-10-0-0-12 wordpress]# cd /mnt/efs
# du --max-depth=1 -h
258M ./ftp
258M .
실제론 그렇지 않다. 일정 GB이상의 데이터가 쌓여야 명령어가아닌 gui에서 확인할수 있다.
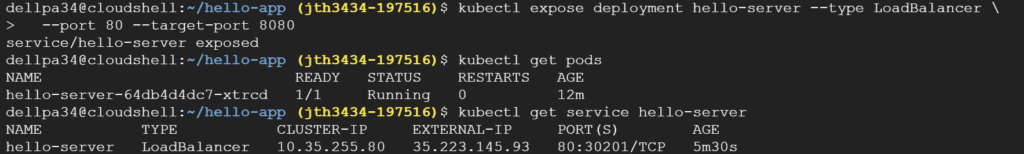
오늘은 이 파일시스템을 백업할거다.
aws backup를 사용할때 유의할점은 백업볼트를 생성할때 각각 목적에 맞게 분할해서 사용하라는 거다. 급하게 작업하다가 관리가 너무 불편해져서 결국 나눴다.
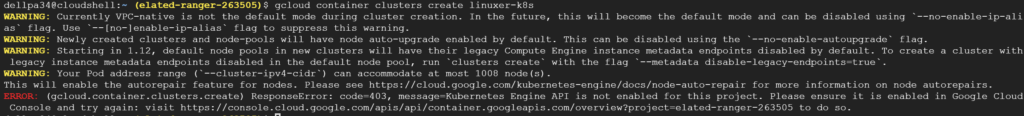
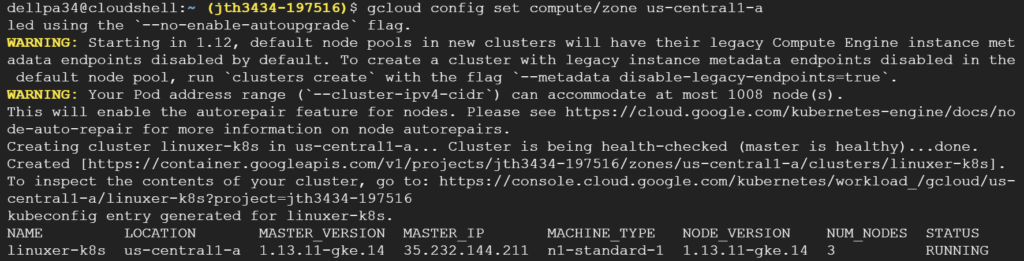
일반적으론 볼트생성->계획생성->규칙생성->리소스할당 순서다.
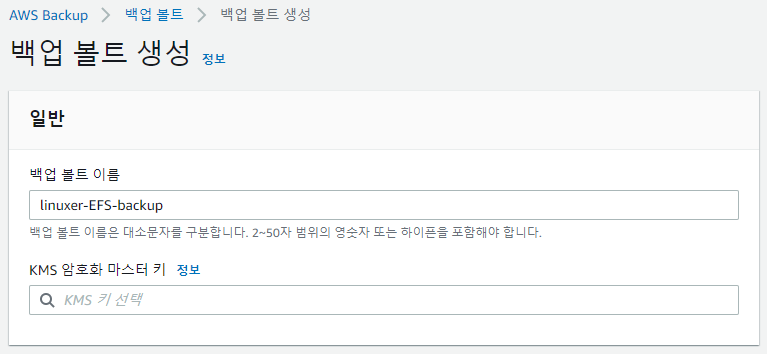
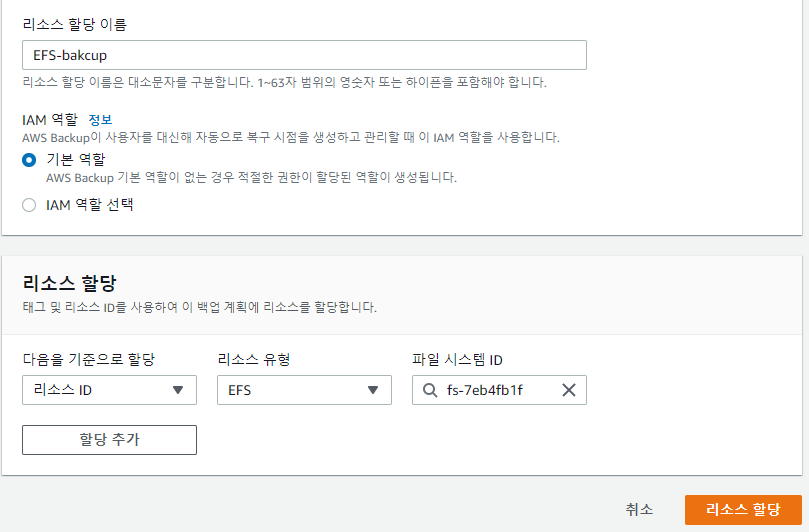
리소스할당은 tag 기반으로도 가능하고 리소스ID 유형으로도 가능하다.
여기까지 백업계획을 이용한 스케줄 백업이었고 단발성 백업은 대시보드에서 온디멘드 백업으로 진행하면 된다.
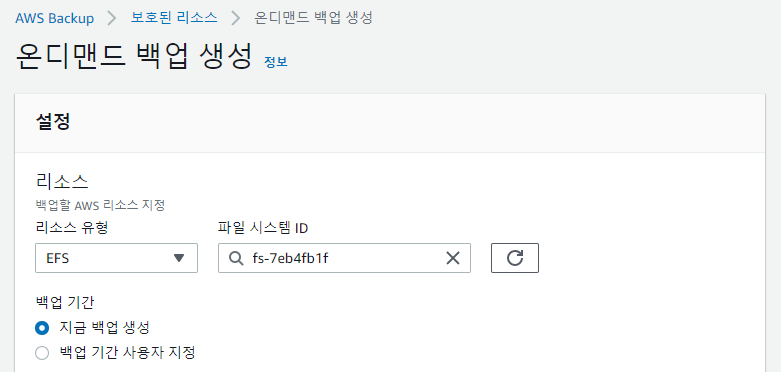
진행중인 jab는 작업부분에서 확인할수 있다.
용량이 작어서 금방 백업이 완료됬다.
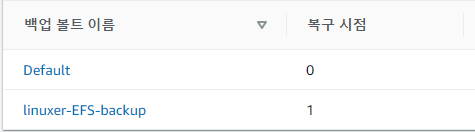
백업은 증분방식이고 복구지점에 카운트가 올라간다.
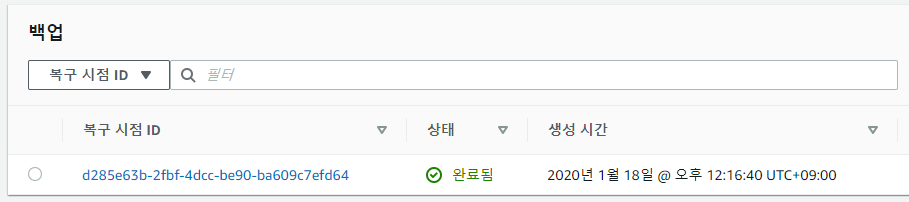
복원을 진행해 보면
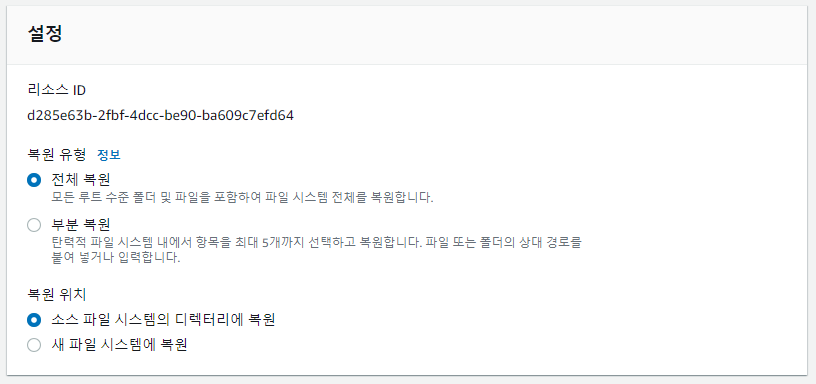
전체/부분/소스/새 이렇게 선택지가 나눠지는데 얼마전 나에게 혼란을 줬던 부분은 전체-소스 파일 시스템에 복원이다.
복원을 누르면 작업탭에 복원에서 확인할수 있다.
Pending-> Running -> Completed 단계를 거친다.
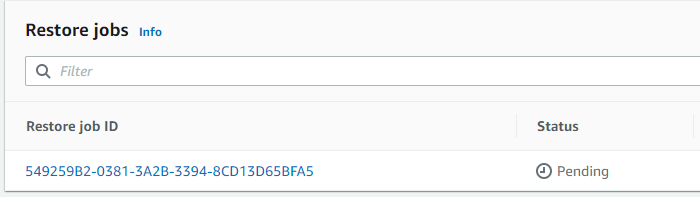
Pending 이 한국어 에선 보류중으로 나오는데 처음에 좀 당황했다.
보류...??????????????????????????????????????????????
하고 Pending 좀 오래걸린다. 거의 10분 이상걸린적도있다.
root@ip-10-0-0-12 ~]# cd /mnt/efs/
root@ip-10-0-0-12 efs]# ll
total 16
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 6144 Jan 18 11:24 aws-backup-restore_2020-01-18T03-33-30-039Z
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 6144 Jan 18 11:24 aws-backup-restore_2020-01-18T03-47-22-912Z
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 6144 Jan 18 11:24 aws-backup-restore_2020-01-18T03-49-03-261Z
drwxr-xr-x 3 jth-ftp jth-ftp 6144 Aug 21 21:20 jth-ftp
aws-backup-restore_2020-01-18T03-33-30-039Z 같은 형식으로 복원 시작시간으로 디렉토리가 생성되고 복원이 된다. 당연히 복원되는 양에 따라서 속도도 다르다.
3번 복원을해서 3개의 디렉토리가 추가 생성된거다. 사용용량이 df 로는 안보이지만 aws 콘솔에선 보인다.

처음 복구할 땐 덮어쓰기로 생각해서 한참을 기다려도 복구가 안되는거같아 EFS의 /를 마운트 해보고서야 알았다. 아 디렉토리 생성 후 복구되는구나.
그래서 이제 추가로 파일 복구를 해보기로 했다.
root@ip-10-0-0-12 wp-admin]# pwd
/mnt/efs/jth-ftp/wordpress/wp-admin
root@ip-10-0-0-12 wp-admin]# ll
total 980
/mnt/efs/jth-ftp/wordpress/wp-admin 디렉토리를 복구해보겠다.

부분 복원으로 선택하고~ 작업은 부분복원이 좀더 걸리는거 같았다.
/mnt/efs/aws-backup-restore_2020-01-18T04-09-39-782Z/jth-ftp/wordpress/wp-admin
경로로 이동해서 복구 확인해봤다.
root@ip-10-0-0-12 wp-admin]# ll
total 980
정상적으로 잘복구 된것을 확인할수 있었다.
efs 를 매우 애용하는 입장에서 파일복구가 가능해진것은 매우 반길 일이다.
아 추가로 EFS 에서 Bursting 모드를 사용할경우 BurstCreditBalance 를 가지게 되고 사용시 소모가 된다. 그런데 백업이나 복구시에는 크레딧을 따로 소모하지 않았다.
읽어주셔서 감사하다!