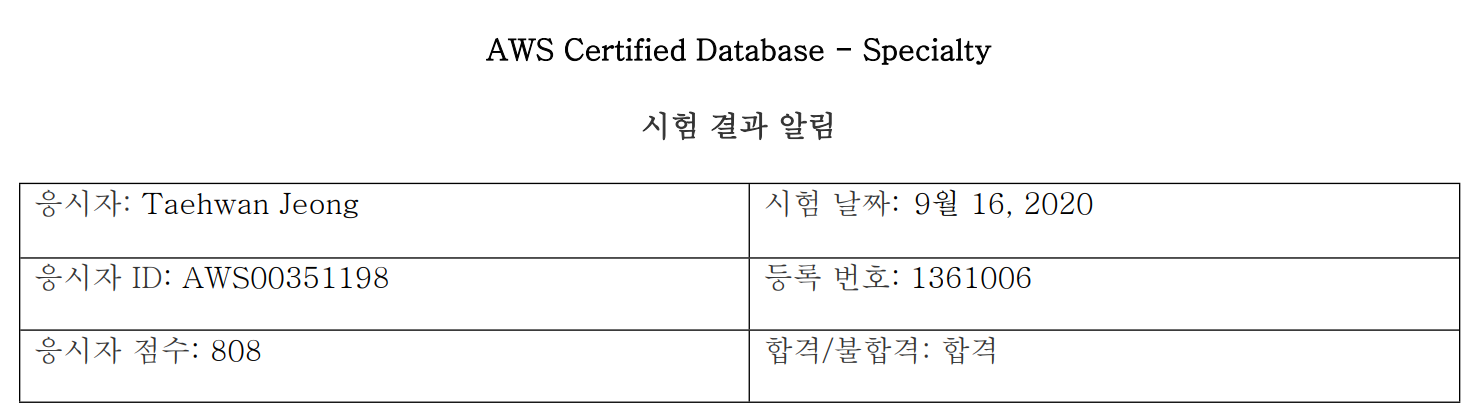
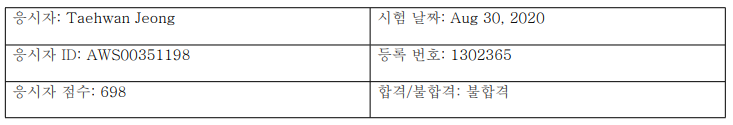
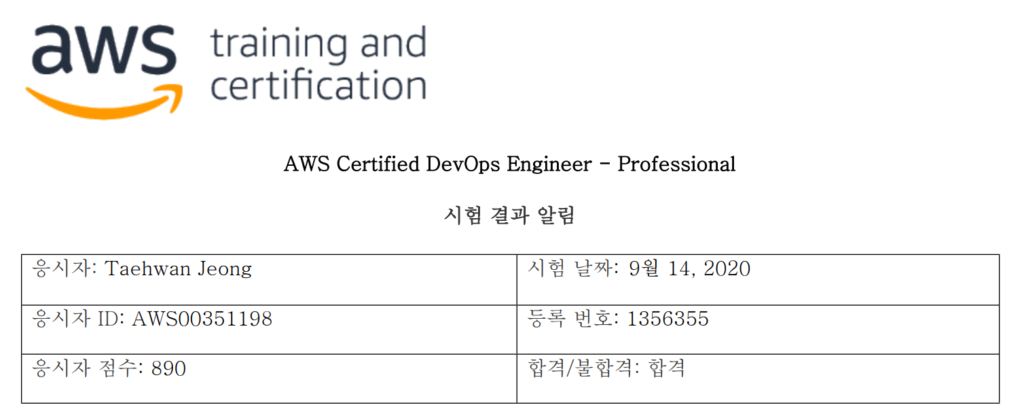
AWS Certified Database - Specialty 시험을 응시했다.
공부를 안하고 먼저 연습시험부터 봤다.

8월 17일 시험을봤다. 오늘까지 한달정도의 텀이 있었고 DOP를 보면서 DBS에 대한 공부도 어느정도 같이 진행이 되었다. 이때 연습시험에서 나온점수는 45%였다.
총점: 45%
주제별 채점:
1.Workload-Specific Database Design:75%
2.Deployment and Migration:0%
3.Management and Operations:50%
4.Monitoring and Troubleshooting:50%
5.Database Security:50%
공부를 하나도 안하고 본 연습시험이라 각이 보였다. 뭐 깊은 고민도 없는 상태였고, 쭉쭉 시험을 풀어나갈수있었기 때문이다.
DOP 시험후 연습시험을 또 봤다. 이시점엔 공부가 어느정도 진행된 상태였다.
공부라함은..DB 서비스들의 docs를 대충보고 FAQ를 탐독하여 어느정도 지식이 있는상태였다. 대부분의 디비를 쓴상태지만.. 넵튠은 넵튠은...! 생소했다. 그래서 좀 열심히 봤는데 이게또 한번 생성하는 거만 못했다. 16일 밤에 부랴부랴 생성해봤다.
총점: 65%
주제별 채점:
1.Workload-Specific Database Design:50%
2.Deployment and Migration:75%
3.Management and Operations:75%
4.Monitoring and Troubleshooting:50%
5.Database Security:75%
20%를 올렸다. 불안감이 엄습했다..허어....70%였으면 불안하지 않았으리라..근데 불안했다. 그래서 연습 시험보면서 봤던 문제들을 기억해서 넵튠 만들고 오로라로 전환하고 테스트를 했다. 오로라 생성이 좀 오래걸려서..새벽2시 까지 봤다. 이과정을 해보길 잘했지 안해봤으면 넵튠 문제 다 틀릴뻔했다.
https://aws.amazon.com/ko/products/databases/
일단 이걸 기반으로 공부해야한다.
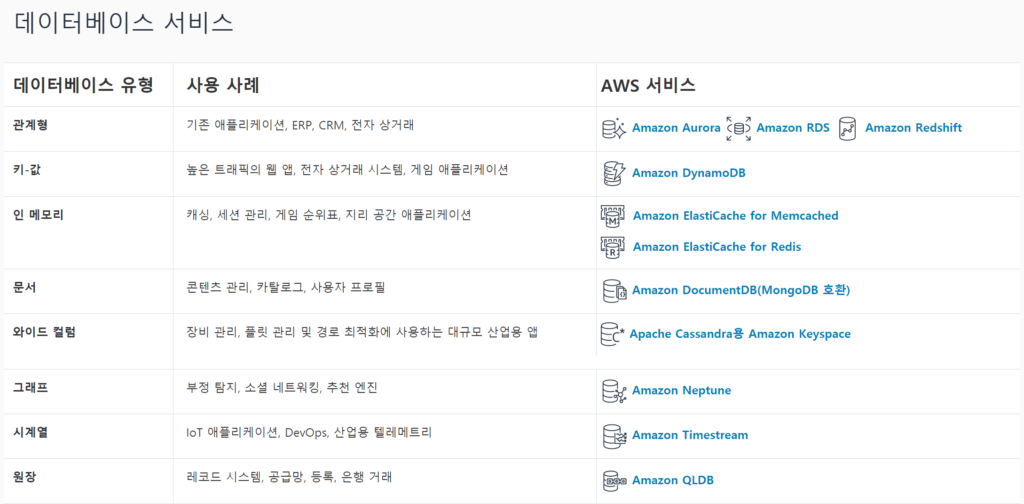
아직 Timestream / QLDB / cassandra 는 시험에 나오지 않는다.
FAQ를 중점적으로 읽고 사용사례를 꼭 읽자.
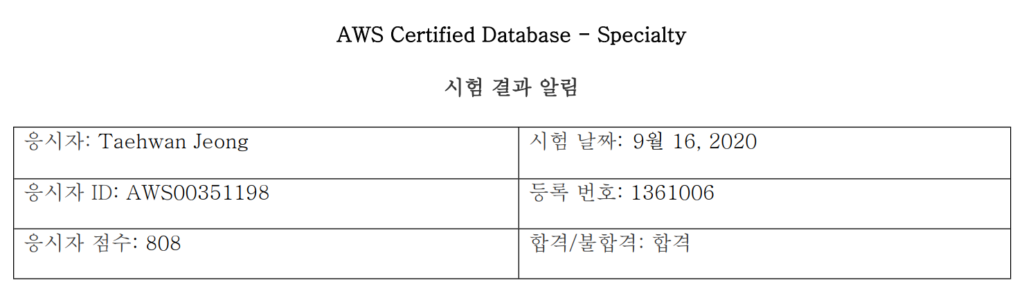
DBS 는 이미 먼저 한번 공부를 했던 su - 현님의 리드가 있었기에 공부가 쉬웠다.
공부에 도움을 주신 su - 현님께 감사를 드린다.

읽어 주셔서 감사합니다.
또 읽어주세요!